What is the carbon content of ductile iron castings?
2025-09-17
A higher carbon content can promote the graphitization of the castings. Since graphite takes on a spherical shape, it can absorb energy in mechanical applications and thus improve the physical properties of the machinery.
The carbon content of ductile iron is generally high, making it an iron-carbon alloy. For industrial cast iron, the typical carbon content ranges from 2% to 3.9%, with a carbon equivalent between 4.1% and 4.7%.Main components of ductile iron castings: The chemical composition of ductile iron primarily includes five common elements: sulfur, phosphorus, silicon, carbon, and manganese.Application of carbon content in ductile iron castings:It is particularly important to note that when preparing the melting materials, if the casting wall is thin and the residual amount of spheroidizing elements is large or insufficiently inoculated, the content should be taken at the upper limit, otherwise, the lower limit should be used. Choosing the carbon equivalent near the eutectic point not only improves the fluidity of the molten iron but for ductile iron, increasing the carbon equivalent also enhances the self-compensating ability of the molten iron during solidification due to the increased graphitization expansion. However, too high a carbon content can lead to floating graphite.
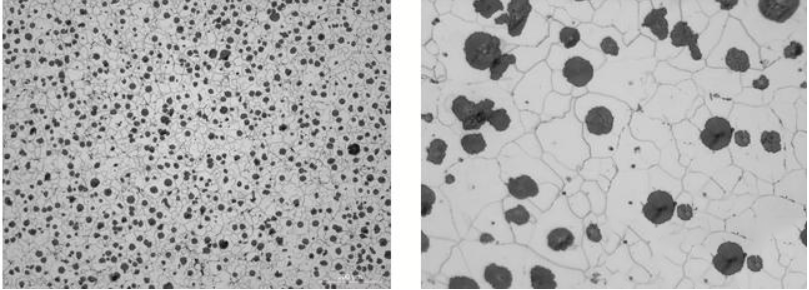
Therefore, based on empirical observation, the upper limit of the carbon equivalent in ductile iron is reached when floating graphite is observed in the molten iron (at a temperature around 1200°C).Impact of carbon content on the performance of ductile iron:The carbon content in ductile iron castings affects the amount of graphite precipitated during solidification, which refers to the average size or number of the graphite spheres. Typically, the carbon content of ductile iron castings ranges between 2% and 3.9%, but it is crucial to understand the impact of reducing carbon content on the mechanical properties of cast iron. This should be considered based on the structure, dimensions, wall thickness, and the errors in the wall thickness of adjacent plane walls of the ductile iron castings. Reducing the carbon content in ductile iron from about 4% to 2.5% can slightly increase tensile strength and yield strength (around 23 to 31 N/mm²) and also increases elongation by about 5%, with significant improvements in impact values.




